HallTech is transferring a core technology from space to redefine physical vapour deposition processes on Earth. By leveraging a modified electrical propulsion device currently used to manoeuvre satellites – the Hall-effect thruster – the team will enable the production of next-generation renewable energy solutions. Participating in the programme of ESA’s Dutch business incubator (ESA BIC Noordwijk), the company is developing an ion-beam source to enable high-quality deposition of dielectric materials, which are critical for advanced applications in semiconductors, flexible displays, batteries and solar cells.
Physical vapour deposition (PVD) describes a group of thin film deposition techniques that involve vaporising a solid material in a vacuum, then depositing that material onto a substrate. Coatings created in this manner are highly durable and resistant to scratching and corrosion. The production of next-generation renewable energy solutions, such as solar cells and solid-state batteries, relies heavily on PVD. However, current PVD methods fall short, for example magnetron sputtering and deposition sacrifices quality for throughput, while semiconductor-grade ion beam sputtering and deposition sacrifices throughput for quality.
The co-founders of HallTech – CEO Olivier Oomen and CTO Andrey Nikipelov – have a novel solution that fills the gap between magnetron and gridded ion beam sputter and deposition. With a business idea for repurposing a space technology in this way – through a downstream technology transfer process – it was a logical next step for the startup to head to ESA BIC to develop the idea. After founding the company in 2023 and joining ESA BIC Noordwijk in late 2024, the team is now collaborating with aerospace engineers and on track to receive technical support from ESA during the incubation programme. We caught up with Olivier to find out more.
What is your focus and how does HallTech stand out?
We are driving innovation with superior PVD processes. HallTech’s gridless source offers the productivity of magnetron sputtering with the film quality of a gridded ion beam system. Our process is tailored for deposition of pure, particle-free, dielectric coatings – even on fragile or heat-sensitive substrates – while being 10x more energy efficient due to utilisation of untapped parameter space.
What is your background and the make-up of your team?
Both myself and Andrey have a background in applied plasma physics. We met during our time working at ASML, where the main focus was removing materials using plasma. This was when we realised that there was a gap in the available technologies to actually deposit materials using plasma, and that these current technologies are very outdated and limit the innovation of advanced manufacturing. So, we set out to solve this.
What problem is your solution addressing?
Today’s coating tools are bottlenecks: they force manufacturers to choose between throughput and quality. HallTech eliminates that, helping the industry step up production. Specifically: advanced products require superior coatings, that often are possible technologically but are prohibitively expensive. The current technologies are simply not good enough. We are developing a new PVD technology that enables superior coatings that are affordable.
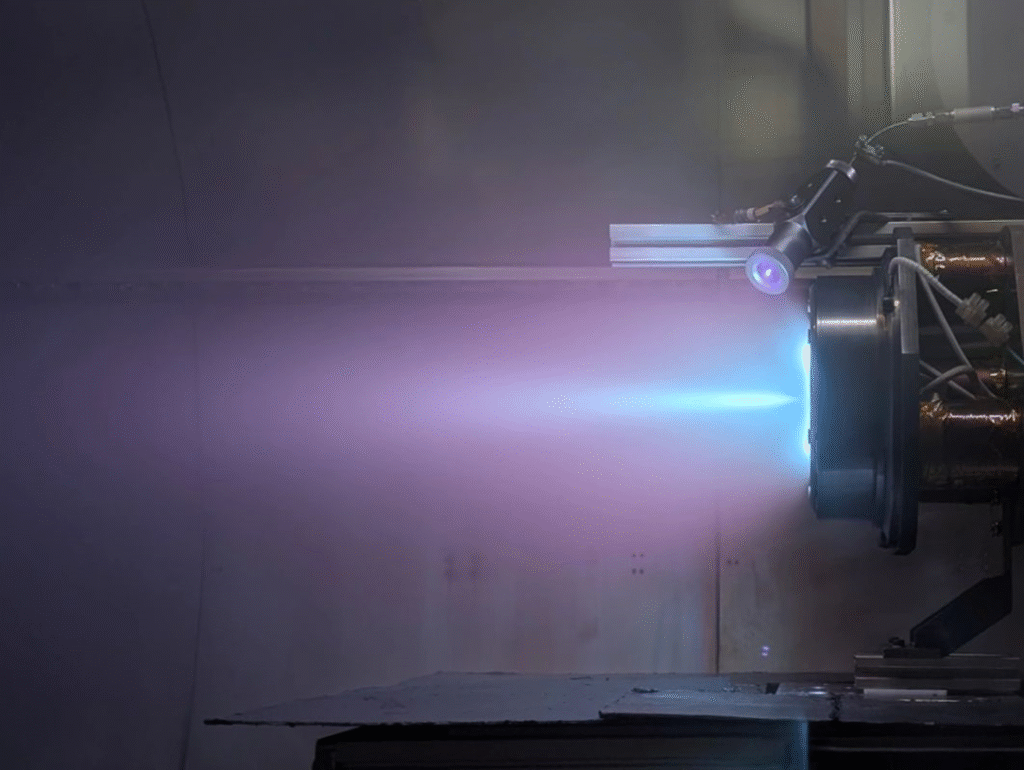
Space tech: The essential working principle of the Hall-effect thruster is that it uses an electrostatic potential to accelerate ions up to high speeds. In a Hall thruster, the attractive negative charge is provided by an electron plasma at the open end of the thruster. A radial magnetic field is used to confine the electrons, where the combination of the radial magnetic field and axial electric field cause the electrons to drift, thus forming the Hall current from which the device gets its name. Discover more
Can you explain about the space connection?
The core technology that HallTech is using is the Hall-effect thruster (HET), used for manoeuvring satellites in space. However, the plasma plume created by the HET is not designed for PVD, as the environment is completely different. In our team, we have the expertise to make it optimal for PVD applications.

Get financial support (€60K funding) to help launch your space business >>
What stage are you currently at?
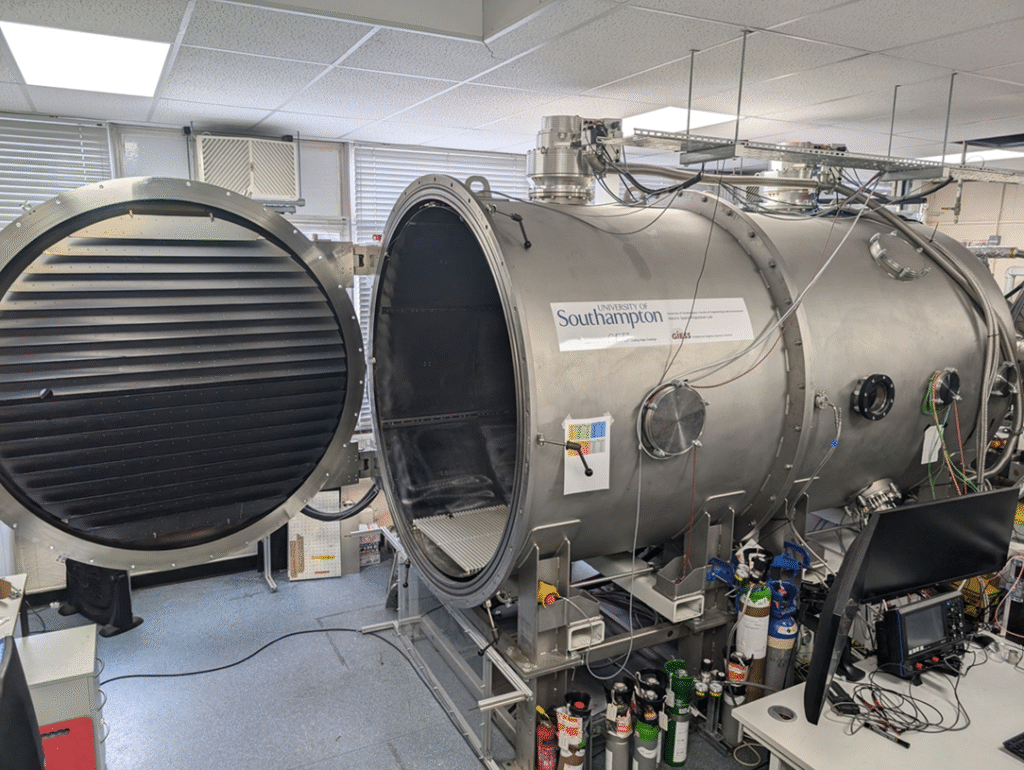
We have designed a device and will be testing it this summer. We recently announced a new partnership with researchers at the University of Southampton to build our first proof of concept (POC) ion source. Together, we’ll validate a production method that finally combines speed, top tier film quality and energy efficiency – critical for next gen dielectric PVD coatings.
What are you initially focusing on during incubation?
Priority is being given to testing the prototype – which is a 5 kW ion source comprising a robust anode technology. Our POC tests have begun this month (June 2025). Alongside this, we are filing patents in the US and EU to protect the core innovations and maintain a competitive edge.
What are the ambitions for your company?
To become the manufacturer for advanced products – basically, we want to produce the go-to technology for this thin film deposition. HallTech is well-positioned to become the preferred PVD solution for high-performance dielectric coatings. Our mission is to bridge the gap between magnetron sputtering and high vacuum ion beam sputtering solutions, facilitating affordable renewable energy generation and storage.
We realised that there was a gap in the available technologies to actually deposit materials using plasma – so, we set out to solve this
Olivier oomEN
What aspects of the ESA BIC programme appeal to you?
We’re excited to be part of the ESA BIC community. I really like the exchanges with the entrepreneurs and sharing challenges. As all the startups are space related, it leads to some interesting discussions. For the rest, it’s mostly about building the company and getting the expertise and technical support. The close connection with ESA is playing a pivotal role in the ongoing success of our technology’s development. Through participation in the ESA BIC programme, we benefit a lot from the access to technical expertise from ESA. We will conduct prototype testing at the propulsion lab at ESA/ESTEC, which has the required infrastructure and machinery to test our innovation.
Would you encourage entrepreneurs to apply to ESA BIC?
If the space ecosystem can help you propel your startup, it is definitely valuable to join the incubation programme. Beyond financial and technical support, ESA BIC can provide the network and momentum needed to bring your business idea to life.

ABOUT HALLTECH
HallTech is at the forefront of developing advanced physical vapour deposition (PVD) technology that eliminates the traditional trade-offs between quality and throughput. This innovative approach is particularly suitable for applications requiring high-quality insulating material coatings and sputtering targets, where conventional methods fall short. HallTech’s proprietary ion-beam sputtering platform enables high-throughput, high-quality deposition of dielectric materials. The technology is designed to be cost-effective, making it an attractive option for industries focused on renewable energy generation and storage. It is applicable for next-generation manufacturing of semiconductors, flexible displays, batteries and solar technologies. halltech.nl
Validate your business plan and space connection!
Refine and validate your space business idea via the space connection assessment takes place as part of your preparation of applying to ESA BIC. Want to find out more? Meet the team & get your questions answered: